Risk Mitigation, Preparedness & Response

Drought mitigation, preparedness and response comprise the appropriate measures and actions aimed at reducing the vulnerability to drought and reducing the impacts of droughts. The goal of the pillar on drought mitigation, preparedness and response is to determine appropriate mitigation and response actions aimed at risk reduction, the identification of appropriate triggers to phase in and phase out mitigation actions, particularly short-term actions, during drought onset and termination and, finally, to identify agencies or ministries or organizations to develop and implement mitigation actions.
The measures can be subdivided into long-term, medium-term or short-term options. Long-term measures are normally included in the development strategies of the concerned sectors; hence, revisiting these strategies to ensure their alignment with drought risk management is an important step when developing a National Drought Management Policy. Medium-term measures are implemented in a timely manner, prior, during and after drought, based on triggers provided by monitoring and Early Warning Systems (Pillar 1). Emergency response measures are implemented if a severe drought occurs with a view to responding to basic needs of the population affected, while contributing to long-term development.
From: WMO/GWP 2018 (not yet published)
IDMP National Drought Mitigation Plan Survey
In 2018 a survey was conducted by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) to assess countries’ advances in drought management planning. All 28 responding countries stated that they had some kind of drought preparedness plan and 18 countries indicated they had drought policies in place. This survey was taken further by IDMP in 2019 by a targeted web search on publicly available information about mitigation measures mentioned in drought plans and policies in the countries that had participated in the 2018 survey.
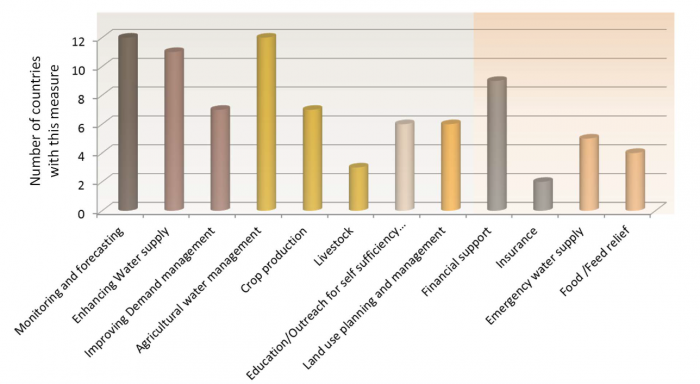
The above graph shows the 12 main groups of mitigation actions that countries mentioned and the number of times each group of mitigation actions was mentioned. The mitigation measure groups were tentatively split into proactive (left) and reactive (right) measures, indicated by different background shading.
More information on survey scope, method and results can be found here.
Examples for Mitigation Measures
The UNCCD Drought Tool Box offers a collection of Mitigation Strategies and Technologies. Additionally, the list below provides some examples of drought preparedness, response and recovery measures that could be included in a National Drought Policy or Plan. The compilation is not exhaustive and should be adapted to local needs as well as integrated with community knowledge (Source: M Bazza, FAO).
| Water resources | |
|---|---|
| Enhancing supply |
|
| Improving demand management (in all sectors/uses) |
|
| Agriculture | |
|---|---|
| Agricultural water management (complying with water resources strategy/plan) |
|
| Crop production |
|
| Livestock |
|
| Other sectors | |
| Municipal water Health Food security Energy Transportation Tourism/Recreation Industry Forest/rangeland fires Education Environment Ecosystem services/ biodiversity |
| Water | |
|---|---|
| Supply augmentation (all/specified sectors) |
|
| Demand management (all/specified sectors) |
|
| Measures other than supply and demand |
|
| Agriculture | |
| Crop Production |
|
| Livestock, range and pasture lands |
|
- Drinking water supply (humans, livestock, wildlife)
- Insurance compensation
- Public aid to compensate loss of revenue
- Tax relief (reduction or delay of payment deadline)
- Rehabilitation/recovery programs
- Food programs
- Feed programs
- Fire control programs
- Resolving conflicts
- Postponing payment of credits
- Implement set-aside regulations


